A new chip crisis?
BURCU KIRATLI/BLOOMBERG HT RESEARCH ANALYST
China’s Ministry of Commerce announced on Monday that gallium and germanium, along with their chemical compounds, will be subject to export controls to protect Chinese national security from August 1. Both metals are indispensable for the manufacture of some chips, the statement said.
China is the dominant global producer of both metals for electric vehicle manufacturers, defense and display applications. Gallium and germanium play a role in producing a series of compound semiconductors that combine multiple elements to increase conduction speed and efficiency.
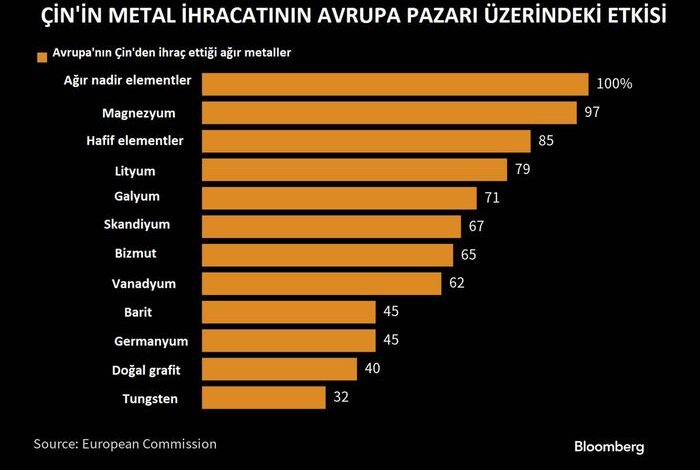
China accounts for about 94 percent of the world’s gallium production. These metals are not particularly rare or hard to find, but China has kept their prices cheap; Currently, it is in a dominant position in the world as a reserve, both by its own production and by exporting it from other countries. Both metals are by-products from the processing of other commodities such as coal and bauxite, which are the basis of aluminum production, and with limited supply, production elsewhere is possible, but costly in the first place, and the European Union supplies 71 percent of its gallium and 45 percent of its germanium to China. takes from
China’s move comes after the US and its allies have increased their rhetoric against the country in recent weeks. Sources close to the matter told US President Joe Biden last week that the administration plans to block the sale of certain chips used to run AI programs. The Wall Street Journal reported that the government is considering new restrictions on the export of advanced chips used in AI computing to China. then, NVIDIA and AMD stocks were negatively affected in that day’s session.
The said export restrictions would be enforced by the Commerce Department and come after the US government had already limited the computing power of chips made for Chinese use. AMD and Nvidia were also affected by the previous limitation. Nvidia responded to previous restrictions by creating a lower spec chip for the Chinese market. However, under the new controls considered, this chip, even the A800, will be restricted from exporting without a license, the Journal reported, and the new restrictions will also apply to companies offering cloud-based computing solutions that are used by some companies to circumvent export controls.
New controls released
This call by the US was answered by the Netherlands, and the government issued new export controls to restrict the shipment of more of chip giant ASML’s chip manufacturing machines to China. While the government did not specifically mention China or ASML in the statement, these measures are designed to restrict shipments of three models of the company’s machines to the Asian country. ASML is one of the most important parts of the semiconductor supply chain and has a nearly monopoly on the machinery that chipmakers need to produce the most advanced chips. The new regulation will force ASML to apply for a license for the export of some advanced deep ultraviolet lithography systems. The measures, published in the Dutch official newspaper on Friday, will come into effect on 1 September, the government said in an emailed statement.
China’s move comes at a time when the EU is embarking on an unprecedented overhaul to eliminate carbon emissions in its entire economy, from energy production to agriculture and transport. The Green Deal, whose goal is to make the region climate neutral by 2050, will require access to massive amounts of critical materials used in everything from solar panels to electric vehicles.
Billion-dollar investments were made to solve the chip crisis in the world. It will take 2024 for all investments to come into play. The radical resolution of the chip crisis will take place in 2025. However, contrary to popular belief, the chip crisis dates back to 2020. Global chip problem; It stems from many reasons, including economic, political and political. One of the main reasons for the crisis is the environment of competition and greed, especially among chip manufacturers. In addition, and most importantly, the need for chips is higher than ever due to the rapid developments in technology in recent years, such as artificial intelligence, internet of things, 5G technology, augmented reality and virtual reality applications, autonomous and electric cars. It is estimated that the size of the semiconductor chip industry, which reached approximately 600 billion dollars in 2022, will exceed 1 trillion dollars in 2030.
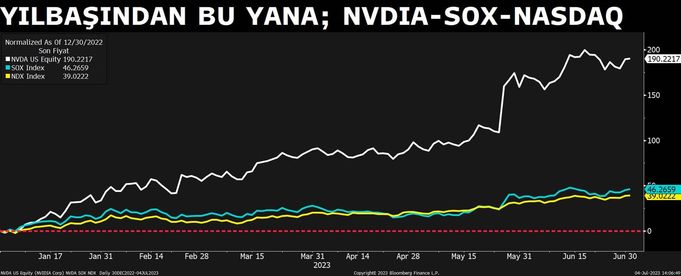
To remember; Nvidia’s shares, in the company’s balance sheet announced on May 24, were reported to be $11 billion in revenue for the next quarter. Market expectations were that it would be at $7.2 billion. The rise in Nvidia’s shares also helped the shares of other chip manufacturers and companies that develop artificial intelligence applications to gain value. In the first 6 months, the rise in the shares of NVDIA increased by 190 percent and the Semiconductor Industry Index (SOX) increased by close to 50 percent, and it was the biggest driving force that made the technology-heavy Nasdaq index rise close to 40 percent this year.